Thursday, April 30, 2009
the History of OHSAS
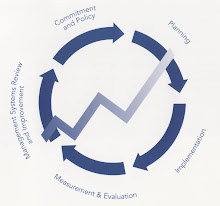
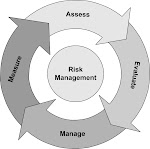
OH&S MS
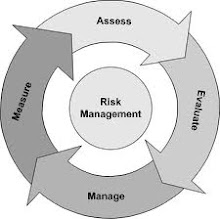
The delicacy is that the findings of a well-conducted risk assessment may challenge the adequacy of well-established standards. Standards are usually designed to be applicable in a wide range of situations, but they may be found unsuitable in some specific contexts. Existing standards may well be found to be either inadequate or over-zealous in these contexts.
The process described is based on the simple model used in BS 8800.
Classification of work activities should involve two stages of categorisation. The first involves classifying all organisational work activities in a manageable way, for example, geographical location, stages in the production process, defined tasks. Care should be taken to include all activities, whether infrequent or day-to day.
Once assessors are sure that all tasks have been listed, information should be gathered about the exact nature of each activity: what, where, how, by whom and so on. Without this knowledge, it is easy to focus on the obvious physical hazards, without the refinement provided by a detailed understanding of the work process in which they exist.
The risk assessment process relies upon thorough and accurate information provided by this initial classification exercise.
4.3.2 Legal and other requirements, examples Besides the Health and Safety at Work Act itself, the following Apply across the full range of workplaces:
1 Managementof Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999:
Require employers to carry out risk assessments, make arrangements to implement necessary measures, appoint competent people and arrange for appropriate Information and training.
2 Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations 1992:
Cover a wide range of basic health, safety and welfare issues such as ventilation, heating, lighting, workstations, seating and welfare facilities.
3 Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992: set out requirements for work with Visual Display Units (VDUs).
4 Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992:
Require employers to provide appropriate protective clothing and equipment for their employees.
5 Provisions and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998:
Require that equipment provided for use at work, including machinery, is safe.
6 Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992: cover the moving of objects by hand or bodily force.
7 Health and Safety (First Aid) Regulations 1981: cover requirements for first aid.
8 The Health and Safety Information for Employees Regulations 1989: require employers to display a poster telling employees what they need to know about health and safety.
9 Employers' Liability (Compulsory Insurance) Act 1969:
Require employers to take out insurance against accidents and ill health to their employees.
OHS04101 ENIN - Course Notes/Issue 1/ Apr 2008
9 of 71
©The British Standards Institution 2007
OH&S MS Auditor/Lead Auditor - Delegate Workbook
10 Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 1995 (RIDDOR): require employers to notify certain occupational injuries, diseases and dangerous events.
11 Noise at Work Regulations 1989: require employers to take action to protect employees from hearing damage. .
12 Electricity at Work Regulations 1989: require people in control of electrical systems to ensure they are safe to use and maintained in a safe condition.
13 Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH): require employers to assess the risks from hazardous substances and take appropriate precautions.
In addition, specific regulations cover particular areas, for example asbestos and lead, and:
14 Chemicals (Hazard Information and Packaging for Supply) Regulations 2002:
require suppliers to classify, label and package dangerous chemicals and provide safety data sheets for them.
15 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 1994: cover safe systems of work on construction sites.
16 Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1994: cover safe installation, maintenance and use of gas systems and Appliances in domestic and commercial premises.
17 Control of Major Accident Hazards Regulations 1999: require those who manufacture, store or transport dangerous chemicals or explosives in certain quantities to notify the Relevant authority.
18 Dangerous Substances and Explosive Atmospheres Regulation 2002: require employers and the self-employed to carry out a risk assessment of work activities involving Dangerous substances.
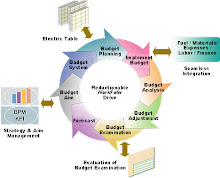
4.3.3 Objectives and programmes Top management shall set OHSAS objectives at relevant levels/functions. These objectives shall be measurable and be in line with the organisation's OHSAS policy.
It shall also show commitment to continual improvement. Once the OHSAS objectives have been set Top management should plan how to achieve these objectives. Top management will need to refer to their initial OHSAS requirements and objectives. All changes are planned and implemented to ensure integrity and improvement is maintained during this change
-
Auditing techniques (some ideas) Have measurable objectives been set for each relevant function/level and consistent with the OHSAS policy? ._ -------
OHS041 01 ENIN - Course Notes/Issue 1/ Apr 2008
10 of 71
©The British Standards Institution 2007
Swine Flu
Swine influenza
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article is related to a current event: 2009 swine flu outbreak. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses. |
Swine influenza (also swine flu) refers to influenza caused by any strain of the influenza virus endemic in pigs(swine). Strains endemic in swine are called swine influenza virus (SIV).
Of the three genera of human flu, two are endemic also in swine: Influenzavirus A is common and Influenzavirus C is rare.[1] Influenzavirus B has not been reported in swine. Within Influenzavirus A and Influenzavirus C, the strains endemic to swine and humans are largely distinct.
Swine flu is common in swine and rare in humans. People who work with swine, especially people with intense exposures, are at risk of catching swine influenza if the swine carry a strain able to infect humans. However, these strains infrequently circulate between humans as SIV rarely mutates into a form able to pass easily from human to human. In humans, the symptoms of swine flu are similar to those of influenza and of influenza-like illness in general, namely chills, fever, sore throat, muscle pains, severe headache, coughing, weakness and general discomfort.
The 2009 flu outbreak in humans is due to a new strain of influenza A virus subtype H1N1 that derives in part fromhuman influenza, avian influenza, and two separate strains of swine influenza. The origins of this new strain are unknown, and the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) reports that it has not been isolated in swine.[2] It passes with apparent ease from human to human, an ability attributed to an as-yet unidentified mutation.[3] The strain in most cases causes only mild symptoms and the infected person makes a full recovery without requiring medical attention and without the use of antiviral medicines.[4]
Contents[hide] |
MORE
Security

Swine flu: WHO raises threat level as disease spreads
Margaret Chan, WHO's director-general, announced the decision late Wednesday to raise the alert level from phase four - signifying transmission in only one country - after reviewing the latest scientific evidence on the outbreak.
"Influenza pandemics must be taken seriously precisely because of their capacity to spread rapidly to every country in the world," she told a media conference in Geneva.
“This change to a higher alert is a signal to governments, to ministries of health and other ministries, to the pharmaceutical and the business communities, that certain actions now should be undertaken with extreme urgency."
“All countries should immediately now activate their pandemic surveillance plans,” she said, calling on them to remain on high alert for clusters of influenza-like illness and pneumonia.
Early detection and treatment of cases and infection controls in all health facilities were critical, she said.
Alert Phase five means that sustained human to human transmission had been confirmed, with widespread community outbreaks, in at least two regions, she said.
European Union health ministers were due to meet in Brussels on Thursday to discuss Europe's response to the emergency.
Chan said international cooperation was particularly important, warning that the H1N1 influenza virus had shown its capacity to spread rapidly to every country in the world.
Fortunately, she said the world is better prepared for an influenza pandemic than any time in history, due to the substantial investments made to prepare for the H5N1 virus, or bird flu.
“For the first time in history, we can track the evolution of
SOURCE
Tuesday, April 28, 2009
ISI Marked - Submersible pumps
SHAKTI PUMPS: AN ISO CERTIFIED MANUFACTURER OF PUMPS & MOTORS
Posted by admin (0) Comment
WELCOME TO SHAKTI PUMPS, ISO CERTIFIED MANUFACTURER OF PUMPS & MOTORS
The company is establised in the year 1982 as a small unit. Shakti Pumps ltd. became a public ltd. company in 1995 and is engaged in manufacturing Submersible pumps along with motors and associated controls panels in the name “Shakti”. Shakti Pumps has successfully developed its cost efficient indigineous technology for manufacture of fully fabricated stainless steel pumps sets with the quality level at par with internationally recognised pump sets. The company has also obtained BIS certificate for ISI mark in 1989 and through continuous process improvement and streamlining the quality system at par the international standards have now acquired ISO:9001:2000 certifications. Shakti Pumps Ltd. takes care of the customer’s need by supplying them the quality product as per international standards for their total satisfaction.
We manufacture and export energy efficient pumps and motors such as submersible pumps, SRN-booster pumps or submersible motors and many more. The company is fully committed to deliver timely and to extend effective services besides maintaining the quality levels. Moving on the packing department which again in a vital stage before the product actually reaches the hands of the end-users.Thoughtfully developed packaging parameters not only provides for safe shipments but also adds to the importance of individual pumps. In pursuit of excellence, the company will adopt practices that support conservation, sustenance and rejuvenation of energy, environment and natural resources.
This would be achieved by educating our people, continual improvement of technology and processes and application of research.This policy has been communicated to all employees and will be made available to public on demand. SHAKTI PUMPS specializes in manufacturing Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps of 3″, 4″, 6″, 8 & 12″ and horizontal openwell Stainless Steel Submersible Pumpsets. Our specialties are Stainless Steel Submersible pump sets from 0.5 H.P. to 60 H.P.
Please also visit www.shaktipumps.com
Category : About Company Blog
Bookmark :
Digg
del.icip.us
Stumbleupon
Redit it
important FEATURES of Indian Electricity Rules
2. Definitions - LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH and EHV Defined
35. DANGER Notices i.e WARNING Signs to be displayed
44 Instructions for restoration of persons suffering from electric shock
44A Intimation of accident
60 Tests for resistance of insulation
64 Use of energy at HIGH and EHV
73 Supply to X-Ray and high frequency installation
Chapter VIII
Overhead Lines
Chapter IX
Electric Traction
Chapter X
Additional precautions for Mines and Oil-fields
122 Requirement for Cables and cabling
Chapter XI
Miscellaneous
Annexure !X - A
Model forms for Inspection Report
Indian Electricity Rules
Monday, April 27, 2009
Mody in a fix
| |||||||
| |||||||
NEW DELHI: Seven years after the post-Godhra communal riots that raged through Gujarat, chief minister Narendra Modi, 15 of his key ministers and The Supreme Court on Monday ordered the Special Investigation Team (SIT), headed by former CBI director R K Raghavan, to carry out the probe which will investigate the role of top Gujarat BJP politicians as well as Sangh Parivar honchos, including Praveen Togadia and Babu Bajrangi. The SIT has been asked to give in its report to the apex court within three months. This sweeping probe into Modi and 62 others was triggered on the basis of a complaint of Jakia Nasim Ahesan Hussain Jafri, widow of ex-Congress MP Ahesan Jafri who was killed by a mob at Gulbarg Society. The investigation order was issued by a Bench comprising Justices Arijit Pasayat and A K Ganguly. Blog: Divisive Modi The order came even before Jafri's counsel Sanjay Parikh and Aparna Bhat coul |
SOURCE
swine flu
| |||||||
| |||||||
NEW DELHI: Alarmed that the deadly swine flu, which has already taken over 100 lives in Mexico, could reach India, the authorities on Monday The scare of a pandemic that could affect millions across the globe, spurred the Indian authorities to put together a containment plan by deploying doctors at nine airports and ports and making it mandatory for all those arriving from the flu-hit countries to undergo checks for fever and throat infection. Given that these are fairly common symptoms for all kinds of ailments, expect some confusion at the airports, especially in Delhi and Mumbai which get maximum traffic from these countries. At these two airports, a team of 32 doctors is being put in place and the screening process is supposed to kick in from Thursday. The other airports indentified for mandatory check-ups are Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Kochi, Jaipur and Goa. Health ministry officials said that throat swabs would be taken and blood samples collected of travellers who complain of upper respiratory tract diseases and fever. Airport authorities, however, said they are still in the dark and are yet to gear up for these checks. |
Bottled water info
Bottled Water Info-Guide
This Info-Guide is intended to direct you to the best information on starting a bottled water operation in Newfoundland and Labrador. It should be read in conjunction with ourBusiness Start-Up Info-Guide which gives additional information applicable to all types of businesses (e.g. incorporation; taxation; human resources; and more).
Canada/Newfoundland and Labrador Business Service Centre
90 O'Leary Avenue
P.O. Box 8687
St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador A1B 3T1
Telephone: 709-772-6022
Fax: 709-772-6090
Toll-free (information): 1-800-668-1010 (in the Atlantic region only)
TTY Toll-free (hearing impaired): 1-800-457-8466
E-mail: info@cbsc.ic.gc.ca
Web site: http://www.cbsc.org/nl
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Associations
Regulations
Programs & Services
Trade Shows
Awards
Books By Mail Service
Additional Resources
SOURCE
Bottled water HACCP
bottled water QC
Billory Brand
Mehak Food and Beverages
Valvada, Gujarat
Dr Ajay Chawan
Saturday, April 25, 2009
TQM is dead, long live ISO 9000
Monday, April 20, 2009
Saturday, April 18, 2009
Dont promote Winners - promote WINNING Teams
Friday, April 17, 2009
recruiting Consultants, apply NOW
ISO 9000, ISO 9001, TS 16949, ISO 14001, Software ISO, Six Sigma
Hello, from "The Pundits of ISO" !!
 Regd Sr Consultants and Regd Lead Auditor ....a rare combination indeed. People who know both sides of the coin - "Auditing and Consulting". Yes registration, indeed matters (see approved iso consultant, registration benefits)
Regd Sr Consultants and Regd Lead Auditor ....a rare combination indeed. People who know both sides of the coin - "Auditing and Consulting". Yes registration, indeed matters (see approved iso consultant, registration benefits)
Quality Catalysts, plays a role of a "Sarathi", "Charioteer", since 1997, by providing ISO 9001, ISO/ TS 16949, ISO 14001, ISO 18001 etc. Consultancy / Training to organizations, in-pursuit of the journey towards achieving customer satisfaction.
Quality Catalysts helps organizations in achieving certification as per ISO 9001, TS 16949, ISO 14001, Software ISO- CMMI, OHSAS ISO 18001, HACCP etc. It helps organizations establish and implement various management techniques using Kaizen, Quality Circles, PPAP, APQP, TPM, FMEA, SPC, SQC, Six sigma etc.
Quality Catalysts is backed by a fleet of highly trained and experienced ISO consultants, engineers, qualified in various fields viz. Electrical, Mechanical, Software, Aeronautical, Electronics, Telecommunications and Chemicals.
QC, has offices/counsellors situated at major cities in India viz. Pune, Mumbai, Nashik, Aurangabad, Kolhapur, Bangalore, New Delhi etc. equipped with experienced ISO Consultants & TS Consultants.
QC personnel, are on the panel of various foreign Certifying Bodies as ISO 9001, ISO / TS 16949 Auditors / Technical Specialist.
 QC has conducted over 1000 third party ISO 9001 registration / certification audits in various industries including, press parts & components, machined components, rubber, mechanical, metallurgy, electrical, software, banks, construction & builders, hospitals, travels, schools, training institutes
QC has conducted over 1000 third party ISO 9001 registration / certification audits in various industries including, press parts & components, machined components, rubber, mechanical, metallurgy, electrical, software, banks, construction & builders, hospitals, travels, schools, training institutes
read MORE
the ENVIRONMENT Information Centre
| ISO 14001 INFORMATION ZONE | |
| The ISO 14000 / ISO 14001 Information Zone |
|
SOURCE
How serious is threat to power grid? Depends who you ask.
- Share/Email
- Tweet This
- 12 Comments
Expert opinion differs widely over a report that the U.S. electric power-grid has been compromised by cyberspies, perhaps from Russia and China, who have installed malware so they can disrupt industrial control systems for electricity distribution in the event of a conflict.
Quoting former and current government officials anonymously, the Wall St. Journal article this week asserts “the espionage is pervasive across the U.S.” and “software tools left behind” in electric-grid systems could be “used to destroy infrastructure components” in the event of war. However, while the electric power grid is seen as vulnerable to cyber-attacks, there's doubt in some quarters the system has been so wholly compromised or could be so easily destroyed.
“No, it isn’t, but it is vulnerable,” says Ed Legge, spokesman for the Edison Electric Institute (EEI), an association representing about 70 of the largest utilities which generate the bulk of the nation’s electricity through complex swatches of eastern- and western-distribution grids and management and control points called Independent System Operators.
“There is hacking,” says Legge. “Hackers are coming after the electrical grid all the time.”
- Related Content
- Energy companies face uphill battle to secure grid
- White House agenda on homeland security
- Lawmakers see cyber-threats to electrical grid
- Oracle WebLogic Suite: A Middleware Foundation for Application GridWHITE PAPER
- China plan hints at technology power ambitions
While EEI has no knowledge that the nation’s interconnected systems have been pervasively compromised by malware that could disrupt it, there are no illusions that the grid is as safe or efficient as it could be.
“The cybersecurity issue is on our radar,” says Legge. “Computers come with that, and as we use them more and more with our systems, and they become more a part of providing electricity, we have to be concerned about it.”
Gregory Reed, professor of electrical-power engineering at the University of Pittsburgh, as well as a technical consultant with experience at Con Edison in New York City, expresses doubts regarding claims of a pervasive compromise of the U.S. electric grid that would allow an attacker to disrupt it through malware.
“It doesn't seem feasible from what I know,” Reed said. No real-time control of the electric grid is coming from the Internet, he says. “It's firewalled and on separate systems,” says Reed. “We're not operating these systems on the Internet.”
But he does think that if there is espionage, it “won't reveal more than how the network is connected, and being able to map the infrastructure is not a threat without knowing how the system is operated and controlled.”
SOURCE















.jpg)





.jpg)

.jpg)








.jpg)

.jpg)













.jpg)


.jpg)









































































































































































































.jpg)

.jpg)











.jpg)















































.jpg)















.jpg)
























































































































.jpg)