Thursday, December 31, 2009
What Are Spam Blogs?
Spam blogs cause various problems, beyond simply wasting a few seconds of your time when you happen to come across one. They can clog up search engines, making it difficult to find real content on the subjects that interest you. They may scrape content from other sites on the web, using other people's writing to make it look as though they have useful information of their own. And if an automated system is creating spam posts at an extremely high rate, it can impact the speed and quality of the service for other, legitimate users.
What We're Doing About Spam
Needless to say, we do not approve of spamming here at Blogger. Below are some of the things we've implemented to remove and reduce spam on our service. We will update this list as we continue our efforts.
Automated spam classifying algorithms keep spam blogs out of NextBlog and out of our "Recently Published" list on the dashboard.
The same classifiers are used to require an extra word verification field on the posting form for potential spam blogs. This makes it harder for spammers to set up automated systems to do their posting, since a human needs to complete this step.
The Flag as Objectionable button in the Navbar lets you notify us of problem blogs that you find, so we can review them and take appropriate action.
Please tell us why you didn't find this helpful. Thanks!
How can we make this better?
Thanks! Your feedback will help us improve our Help Center.
CDC India - TQMC is regd experts
On February 6th, the Washington Post profiled the work of CDC Development Solutions and the MBA Enterprise Corps worldwide and highlighted the unique opportunities for recent MBA graduates to volunteer overseas and have critical impact during the financial crisis. The article noted that, "our own economic recovery depends in part on the financial success of emerging nations." To learn more about the MBA Enterprise Corps and its work around the world, please contact Kate Ahern at kahern@cdc.org.
CDC Development Solutions Builds on Partnership with the Grassroots Business Fund
CDC Development Solutions and the MBA Enterprise Corps are expanding our partnership with the Grassroots Business Fund (GBF). We will continue to field MBAEC Business Advisors in Tanzania, Kenya, and India, and we will field our first Business Advisor to Indonesia in July. GBF—a spinoff of the International Finance Corporation—works to strengthen and expand grassroots enterprises that provide economic access and sustainable services in the most impoverished regions of Africa, Asia and Latin America. GBF provides “patient capital” financing as well as mentoring, strategic assistance, business advice and networking. Its aim is to grow its clients into scalable, sustainable social enterprises. For more information on CDC Development Solutions’ work with GBF, please contact Kate Ahern at kahern@cdc.org.
CDC Development Solutions Extends Partnership with Equatorial Guinea LNG
CDC Development Solutions has extended our partnership with Equatorial Guinea Liquid Natural Gas (EG LNG) to develop the capacity of local firms and build local content in the LNG industry in Equatorial Guinea. CDC Development Solutions provides technical assistance and training on business plan development, bidding and procurement processes, international marketing and sales techniques, introduction of internationally-accepted accounting standards and methods, and increasing adoption of grades and standards for quality control. For more information on our program in Equatorial Guinea, please contact Amanda MacArthur at amacarthur@cdc.org.
The Wall Street Journal Profiles the IBM Corporate Service Corps
The Wall Street Journal has written an article about the Corporate Service Corps and CDC Development Solutions, entitled “IBM Creates Volunteer Teams to Cultivate Emerging Markets.” For more information on the Corporate Service Corps, please contact Kate Ahern at kahern@cdc.org.
Newsletter Subscription
Keep up to date with CDC Development Solutions’ quarterly e-newsletter. Sign-up to receive the CDC Development Solutions Newsletter.
Communications Office
CDC Development Solutions’ communications team can put you in touch with staff in the United States and around the world to provide technical background and information or insights into development challenges. Or, we can help you find the facts or story you need. Please contact our home office for assistance.
CDC Development Solutions1420 K Street, NWSeventh FloorWashington, DC 20005Phone 1-202-872-0933Fax 1-202-872-0923communications@cdc.org
Back to Top
Primary links
About Us
Practice Areas
Global Impact
News & Resources
Get Involved
Site Map
Great leaders


Posted: 30 Dec 2009 01:11 AM PST
John F. Kennedy via last.fm
Check what ‘big minds’ said about leadership. Those quotes will blow your mind!
“It is a well-known fact that those people who must want to rule people are, ipso facto, those least suited to do it… anyone who is capable of getting themselves made President should on no account be allowed to do the job.” Douglas Adams
“If your actions inspire others to dream more, learn more, do more and become more, you are a leader.“ John Quincy Adams
“No man will make a great leader who wants to do it all himself, or to get all the credit for doing it.” Andrew Carnegie
“Management works in the system. Leadership works on the system.” Stephen R. Covey
“A leader is best when people barely know he exists, not so good when people obey and acclaim him, worse when they despise him….But of a good leader who talks little when his work is done, his aim fulfilled, they will say, “We did it ourselves.”
Lao Tzu
“I am more afraid of an army of 100 sheep led by a lion than an army of 100 lions led by a sheep.“ Talleyrand
“A boss creates fear, a leader confidence. A boss fixes blame, a leader corrects mistakes. A boss knows all, a leader asks questions. A boss makes work drudgery, a leader makes it interesting. A boss is interested in himself or herself, a leader is interested in the group.” Russell H. Ewing
“Becoming a leader is synonymous with becoming yourself. It is precisely that simple, and it is also that difficult.” Warren Bennis
“Leadership and learning are indispensable to each other.” John Fitzgerald Kennedy
‘The best executive is the one who has sense enough to pick good men to do what he wants done, and self-restraint to keep from meddling with them while they do it.” Theodore Roosevelt
“Management is doing things right; leadership is doing the right things.” Peter F. Drucker
“Nothing so conclusively proves a man’s ability to lead others as what he does from day to day to lead himself.” Thomas Watson
‘Only one man in a thousand is a leader of men — the other 999 follow women.“ Groucho Marx
“You do not lead by hitting people over the head – that’s assault, not leadership.” Dwight D. Eisenhower
via 14 leadership quotes that will blow your mind Coool-Stuff.
Key traits of great leaders
Wednesday, December 30, 2009
Calculate and offset your carbon footprint now
Go HERE
Make a Year-End Donation
Dec. 31 is near! Make a tax deductible, year-end donation, and help fight global warming now!
Certify Your Product
Leading companies like Motorola, Florida Crystals and Anvil are benefiting from CarbonFree® Certification.
Return to Forest
Restoring habitats & fighting climate change by reforesting critical biological corridors of Nicaragua.
Give Green
CarbonFree® Products
Featured Project
5S Fundas
5S Photos
Step 1: Sort - "When in doubt, move it out!"
Messy Office - Cluttered, 5S Station - Sign gives clear Red Tagged Items - Unneeded disorganized office in need of instructions on how to sort out office furniture in designated transformation to high unneeded office supplies and "red tag area" is ready for pick up performance work station. furniture. by Surplus Services.
Step 2: Shine - "The best cleaning is to not need cleaning"
Clean Office - The once cluttered Clean Award - An office that truly Shining in action - After sorting, and disorganized office has been shines wins the "Mr. Clean Award" Marianne Bouska scrubs her desk cleaned to shine. at DEED. until it shines.
Step 3: Set in Order - "A place for everything and everything in its place."
Organized Drawer - Office Point- of- Use - Printer paper is Office Supply Station - Common supplies are neatly organized in located directly above the printers office supply area for paper clips drawer. at the point-of-use. and forms to avoid desk clutter.
Step 4: Standardize - "See and recognize what needs to be done."
Labeled Cabinets - Labels on Color Coded Files - Visual Map of Files - Map of files in the outside of the cabinets system for quickly locating workstation where anyone can tell exactly what is inside. files in the file cabinet. easily find files.
Step 5: Sustain - "The less self-discipline you need, the better."
5S Circle - The 5S circle illustrates the commitment required for sustaining a highly efficient workspace.
5S Definition
Back to top
Source
DRUPAL - SEO
This module provides a checklist of good Drupal SEO (Search Engine Optimization) best practices. Maximize the presence of your Drupal website in the major search engines like Google, Yahoo, Bing, etc. It provides a checklist that helps you keep track of what needs to be done. First, it will look to see what modules you already have installed. Then, all you have to do is go down the list of unchecked items and do them. When all the items are checked, you're done!
Some have asked me why this is a module instead of just a list on a website somewhere and that's a fair question. The reason is that many Drupal developers (coders, designer, etc.) work on many sites at the same time. It can be difficult to keep up with everything you've done on each site. Many will take over the SEO on a site that they didn't build and it's time-consuming to go through and figure out what's been done. So, with this module, all you have to do is check the checklist and you know exactly what was done. Further, it places a date stamp next to each item as you complete it so now you have a complete record that you can show clients or refer to in the future. It's more than just a list of stuff to do - it's a powerful organization tool, as well.
Upgrading from 1.x
If you are upgrading from the previous SEO Checklist 1.x versions, you willneed to follow a couple important steps:
Make sure you remove the entire SEO Checklist module's folder before copying in the new files (should be sites/all/modules/seo_checklist).
Execute the following SQL in your site's database, making sure to prefix the 'system' table name if your site uses a table prefix:UPDATE system SET name = 'seochecklist', filename = REPLACE(filename, 'SEOChecklist', 'seochecklist'), status = 1 WHERE type = 'module' AND name = 'SEOChecklist'
Make sure you run update.php immediately afterwards.
Recommended Modules
Vertical Tabs to help improve your SEO Checklist interface. It helps collapse the interface into vertical tabs instead of one huge long list of fieldsets. This module also works on the add or edit content forms, which is helpful for your site's content creators and editors!
This module is paid for and maintained by Volacci, the Drupal SEO company. If you've done everything in the module and you're still not getting the results you're expecting, please contact us. We're here to help make Drupal the best platform on the planet for SEO!
Here's a video from June, 2009 on how to use the module and do SEO on your site: http://budurl.com/ft43
Downloads
Recommended releases
Version
Downloads
Date
Links
6.x-2.0
Download (11.67 KB)
2009-Aug-07
Notes
5.x-2.0
Download (11.22 KB)
2009-Aug-07
Notes
Development releases
Version
Downloads
Date
Links
6.x-2.x-dev
Download (13.28 KB)
2009-Dec-09
Notes
View all releases
Resources
View usage statistics
Development
View pending patches
Browse the CVS repository
View CVS messages
Report a security issue
Source
important LINKS from CDC India
0&&parent.frames.length) {
d=parent.frames[n.substring(p+1)].document; n=n.substring(0,p);}
if(!(x=d[n])&&d.all) x=d.all[n]; for (i=0;!x&&i
function checkit()
{
if(document.form3.str.value=="")
{
alert("Please enter text in search box");
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
Structured Search>>
Sites pertaining to Government of India
Ministry of Commerce
Export-Import Policy of India
Ministry of Industry - Dept of Industrial Policy & Promotion
Indian Commercial Missions Abroad
Indian Missions & Posts Abroad
Others Ministries & Departments
Internet sites of Indian Missions Abroad
Embassy of India, Beijing, China
Embassy of India, Mexico
Embassy of India, Qatar
Embassy of India, Washington DC
Consulate General of India, Hong Kong
Consulate General of India, New York
Consulate General of India, San Fransisco
Consulate General of India, Sao Paulo - BRAZIL
Consulate General of India, Frankfurt
Embassy of India, Bangkok
Embassy of India, Bonn
Embassy of India, Nepal
Embassy of India, Peru
High Commission of India, Ottawa
India Economic News (Embassy of India, Washington)
Embassy of India, Jakarta
Embassy of India, Bratislava
Embassy of India, Kuwait
Embassy of India, Abu Dhabi
Embassy of India, Kathmandu
Embassy of India, Moscow
Embassy of India, Croatia
Embassy of India, Bahrain
High Commission of India, Brunei Darussalam
Embassy of India, Saana, Yemen
Apex Trade/Industry Bodies/Chambers of Commerce
Federation of Indian Export Organisations
Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI)
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII)
Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry
Indo-German Export Promotion Project
ASSOCHAM
FICCI
Indian Merchants' Chamber
The Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry
Export Promotion Councils
Basic Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Export Promotion Council (CHEMEXCIL)
CAPEXIL
Enginnering Export Promotion Council (EEPC)
Overseas Construction Council of India (OCCI)
Foreign Investment Promotion Board
Indian Investment Centre
Banks & Financial Institutions
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
HSBC
ICICI Bank
Indian Bank
IndusInd Bank Ltd
Industrial Development Bank of India, IDBI
Industrial Development Bank of India
Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. IIBI
Oriental Bank of Commerce
Punjab National Bank (PNB)
Standard Chartered
State Bank of Bikaner & Jaipur
State Bank of India
The South Indian Bank Ltd.
UCO Bank
UTI Bank
Union Bank of India (UBI)
Vijaya Bank
Securities and Exchange Board of India
National Centre for Trade Information (NCTI)
Export Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank)
Internet Sites outside India
CBI (Centre for the Promotion of Imports from Developing Countries)
World Trade Organisation
Hong Kong Trade Development Council
Government Supplies Department Procurement Division, HONG KONG
International Trade Centre UNCTAD/WTO - Geneva, Switzerland (ITC)
United Nations Industrial Development Organization - Vienna, Austria (UNIDO)
World Bank - Washington, USA (IBRD)
International Chamber of Commerce
US Customs Service Web Site
The Federation of International Trade Associations (FITA)
Source
Powermaster Tools
English
Español
Français
Russian
Corporate Profile
Introduction
Business Philosophy
Our Mission
Quality
Products
Tube Tools
Bolting Tools
Spring Balancers
Downloads
Events
Shipment
Careers
Contact Us
Head Quarters
Sales & Service
Manufacturing
International Sales
Feedback Form
Spring Balancers, Tool Balancers, Load balancers, power sockets, impact sockets, castellated sockets, spring balancer, slugging wrenches, impact socket, striking wrenches, tube cleaner, slug wrenches, castellated wrenches, powermaster impact sockets, hammering wrenches, podger spanners, tube cleaners, tube cleaning, sugar factory tube cleaners, sugar factory tube cleaning, Tool Balancers, sugar mill tube cleaners, boiler tube cleaners, heat exchanger tube cleaners, heat exchanger tube cleaning, tube cleaning tools, internal tube cleaning, tube descaling tools, tube expanders, tube expander, boiler tube expanders, condenser tube expanders, tube runner, nut splitters, tube installation tools, flange spreaders, hydraulic flange spreaders, hydraulic nut splitters, hydraulic tube pullers, hydraulic tube pulling, tube end facers, tube facing tools, tube puller, tube pulling systems, heat exchanger tube expanders, tube expansion systems, electric tube expansion system, hydraulic tube expansion systems, pneumatic tube expansion drives, pneumatic rolling drives, right angle rolling drive, tube facing machines, pipe facing machines, pipe bevellers, pipe bevelling machines, weld prep machines, serrating tools, grooving tools, tube bundle inserter, tube sheet hole reamer, tube facers, hydaulic torque wrenches, bolt tensioners, bolt tensioner, bolt tensioner pumps, torque multipliers, pneumatic torque wrenches, pneumatic torque multipliers, stud tensioners, hydraulic wrench, electric tube cleaners, pneumatic tube cleaners, bolting tools, torque wrenches, torque multipliers, tube guide, tube pilot, tube leak detector, tube joint testing, tube removal tools, hydraulic stub,
Powermaster manufactures 3 distinct product lines:
Tube Tools: For use in the manufacture and repair of Heat Exchangers,
Boiler Condensers and other tubular apparatus.
Bolting tools: For use to tighten/loosen threaded fasteners to precise
torque.
Spring Balancers/Load Balancers/Tool Balancers: To suspend loads for
easy maneuverability and avoid operator fatigue.
Tube Tools
Tube Expanders
Tube / Pipe Bevelling and Facing Machines
Tube Installation Tools
Tube Expansion Systems
Tube Removal Tools
Tube Cleaners
Bolting Tools
Impact Sockets and Accessories
Slugging / Striking Wrenches
Hydraulic Bolt Tensioners
Hydraulic Torque Wrenches
Pneumatic Torque Wrenches
Backup Wrenches
Mechanical Torque Wrenches
Mechanical Torque Multipliers
Hydraulic Nut Splitters
Hydraulic Flange Spreaders
Pneumatic Impact Wrenches
Spring Balancers / Load Balancers/Tool Balancers
Spring / Load Balancers
Get Videos of Product Demonstration and Catalogs on a CD-ROM. click here
© Copyright. POWERMASTER LIMITED. All rights reserved
Email: sales@powermaster.in
Source
Friday, December 25, 2009
Windows disk Clean up systems
To free some space on your hard disk for better purposes, you have to do a disk cleanup. With the Disk Cleanup utility (Start Menu, All Programs, Accessories, System tools) you have a build in tool to remove many unnecessary files from your hard disk. Select the C: drive and on the first tab check all items to delete.
However, the cleaning is not thorough, especially the 'temporary (internet) files' folders (used files from the last few days will not be cleaned)! It is better to clean them yourself as well, as shown below. Most files are system files and/or hidden, so make sure you can see those type of files in the Windows Explorer (Tools, Folder Options, tab View, enable Display the content of system folders, enable Show hidden files and folders, disable Hide extensions for known file types and disable Hide protected operating system files).
google_protectAndRun("render_ads.js::google_render_ad", google_handleError, google_render_ad);
google_protectAndRun("ads_core.google_render_ad", google_handleError, google_render_ad);
box('../','');
DELETE INDEX.DAT FILES MANUALLY
Disk Cleanup doesn't always work correctly, especially when the index.dat file is corrupt. Another reason to delete the files manually in the Windows Explorer.
boxend('../','');
C:\HIBERFIL.SYS (hidden, as big as the main memory)
This file is created by the hibernation option (Control Panel, Power Options, tab Hibernate). With this option you are able to hibernate your computer. When your computer hibernates, it stores the main memory into the hiberfil.sys file on your C: partition before it shuts down. When you turn on the computer, it returns to its previous state by reloading the main memory with the information in the hiberfil.sys. To turn off this heavy disk consuming option, disable the Enable hibernation option on this tab.
C:\System Volume Information (hidden, also on other partitions)
These hidden system folders contain information for the Windows XP System Restore function. When you are finished with the setup of your Windows system and everything is working error free, I advise to turn off the system restore (Control Panel, System, tab System Restore). Enabling the option Turn off System Restore on all drives will empty all System Volume Information folders. It's difficult to remove the empty system folders from NTFS partitions (FAT32 partitions are no problem).
C:\PAGEFILE.SYS (Virtual memory)
The pagefile is only used when your main memory has been consumed by the running applications and more memory is needed. The use of the pagefile is temporary. Disabling the pagefile is only a wise thing to do if the available memory exceeds 512 MB (the use of the pagefile depends on the demand for memory of the running applications). You can also move the pagefile to another (faster) partition (as suggested on the page Windows XP settings part I) to make a quicker system backup/recovery possible.
C:\WINDOWS\Prefetch
This folder contains information about the regular started applications. Without any problem, you are allowed to delete the files in this folder (the files in the prefetch folder will be rebuild after a restart of Windows). The prefetch files in this folder are used for 'preloading' applications to start them quicker. At first you will probably notice a slower start of your favorite applications, but this will quickly be restored.
C:\Windows\$NtUninstall...... folders (hidden)
Those hidden "$" folders are waiting (and waiting.....) for a Windows update-uninstall. Of course, this will probably never happen! If Windows is working properly and stable after the latest Windows updates, you can delete those folders. The folder $hf_mig$ is the only exception to this rule. It is advised to keep this folder as it is, although removing it doesn't result in problems.
C:\I386\C:\Windows\Driver Cache\I386\C:\Windows\ServicePackFiles\I386\
Do you really want to save space? Delete above folders (or burn them on CD), but at your own risk! The I386 folder contains setup files (including hardware drivers). If everything is working properly, you won't need them, but if your system needs a change you might!
C:\Windows\Downloaded Installations\C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download\
These folders contain the setup files of downloaded and installed applications and Windows updates. The last one contains the downloaded Windows updates, which are there in strange names without any extension. With most of those files you can add MSI or EXE and run them separately. Saving these files makes it possible to patch them on another Windows system or Windows setup files.
Other temporary files (if still present, including the index.dat file):
C:\Documents and Settings\your username\Local Settings\TempC:\Documents and Settings\Default User\Local Settings\TempC:\Documents and Settings\LocalService\Local Settings\TempC:\WINDOWS\TEMP
C:\Documents and Settings\your username\Local Settings\Temporary Internet FilesC:\Documents and Settings\Default User\Local Settings\Temporary Internet FilesC:\Documents and Settings\LocalService\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files
C:\Documents and Settings\your username\Local Settings\HistoryC:\Documents and Settings\Default User\Local Settings\HistoryC:\Documents and Settings\LocalService\Local Settings\History
box('../','');
ERASING FILES WITH ACTIVE@ ERASER
I have very good experience with the Active@ Eraser for Windows application (download: www.active-eraser.com). With this utility you are able to delete your Internet & Local Activities. It will permanently delete files like temporary files, history files, recycle bin, cookies, auto complete lists and other personal settings. This is done by deleting the files and overwrite them with useless info (so you are not able to recover them anymore, even with data recovery software). With this application you are also able to erase already deleted files (read: the empty space) from your hard disk. The free version will overwrite the surface with zeros. (I prefer to use this tool before defragmenting and creating a system backup, it saves time and gives a smaller backup).
boxend('../','');
box('../','');
DELETING LOCKED FILES
Sometimes it's not possible to delete or move a specific file or folder because the file or folder is locked by a specific process. To find out which process is locking it, you can try to find out and stop the process with Process Explorer (download: www.microsoft.com/technet/sysinternals/ProcessesAndThreads/ProcessExplorer.mspx). The process can also be stopped with the Windows Task Manager (combine the keys CTRL-ALT-DEL), tab Processes. With the tool Unlocker (download: http://ccollomb.free.fr/unlocker) it is possible to unlock files and folders by stopping the locking process. If it isn't possible to stop the locking process, then the MoveOnBoot utility can be handy (download: www.gibinsoft.net, see FileUtililties, old version is freeware). This utility makes it possible to move or delete files at the next boot.
boxend('../','');
box('../','');
SEARCHING FOR POTENTIAL HARD DISK SPACE...
At this page many unnecessary folders/files are mentioned, which is a good start. If this still doesn't give you enough free space for you, it's time to do some further analysis to delete some extra files and/or folders (or if you are just curious...). The utility Disktective (download: www.freebyte.com/disktective) gives you this opportunity. Disktective shows by means of pie pieces the use of your hard disk. Another interesting utility is SpaceSniffer (download: www.uderzo.it/main_products/space_sniffer/), which shows rectangles.
boxend('../','');
menurechts('../');
Menno Schoone
Windows XPWindows Vista(Re)installing WindowsPartitioningFree virusscan softwareFree firewall software(Wireless) networkBackup data, drivers,...Backup/synchronisation
Source
Wednesday, December 23, 2009
Vacancy for Sailors
If you have candidates below,
Please send a job application and CV immediately to email address (hroyachmad@yahoo.com or oceanic_island@yahoo.co.id)
- Chief Officer
- 2 nd Officer
- Bosun
- Oiler
The candidate must have been experiences on AHTS.
Thanks for your attention
Best Regard
Roy Achmad
Yossindo Putera Permai PT
Tlp : +62 21 4352403
Fax : +62 21 43901648
Mobile : +62 81 11191049
Website: www.yossindo.co.id
Tuesday, December 15, 2009
HACCP Standards
HACCP standard
1. Location requirements of HACCP
Location requirements of HACCP
Clause 4.1
1. Establishments
Potential sources of contamination need to be considered when deciding where to locate food establishments, as well as the effectiveness of any reasonable measures that might be taken to protect food. Establishments should not be located anywhere where, after considering such protective measures, it is clear that there will remain [...]
2. HACCP requirements of premises and rooms
HACCP requirements of premises and rooms
Clause 4.2
1. Design and layout
3. Equipment requirements of HACCP
Equipment requirements of HACCP
Clause 4.3
1. General
Equipment and containers (other than once-only use containers and packaging) coming into contact with food, should be designed and constructed to ensure that, where necessary, they can be adequately cleaned, disinfected and maintained to avoid the contamination of food. Equipment and containers should be made of materials with [...]
4. HACCP requirements of facilities
HACCP requirements of facilities
Clause 4.4
1. Water supply
An adequate supply of potable water with appropriate facilities for its storage, distribution and temperature control, should be available whenever necessary to ensure the safety and suitability of food.
5. CONTROL OF FOOD HAZARDS in HACCP
CONTROL OF FOOD HAZARDS in HACCP
Clause 5.1
Food business operators should control food hazards through the use of systems such as HACCP. They should:
6. KEY ASPECTS OF HYGIENE CONTROL SYSTEMS in HACCP
KEY ASPECTS OF HYGIENE CONTROL SYSTEMS in HACCP
Clause 5.2
1. Time and temperature control
7. INCOMING MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS in HACCP
INCOMING MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS in HACCP
Clause 5.3
No raw material or ingredient should be accepted by an establishment if it is known to contain parasites, undesirable micro-organisms, pesticides, veterinary drugs or toxic, decomposed or extraneous substances which would not be reduced to an acceptable level by normal sorting and/or processing. Where appropriate, specifications for raw materials should [...]
8. HACCP requirements of packaging
HACCP requirements of packaging
Clause 5.4
Packaging design and materials should provide adequate protection for products to minimize contamination, prevent damage, and accommodate proper labelling. Packaging materials or gases where used must be non-toxic and not pose a threat to the safety and suitability of food under the specified conditions of storage and use. Where appropriate, reusable [...]
9. Water requirements of HACCP
Water requirements of HACCP
Clause 5.5
1. In contact with food
Only potable water, should be used in food handling and processing, with the following exceptions:
Published by admin on Nov 16, 2009 under HACCP standard |
Source
Monday, December 14, 2009
Google adwords payment address
Amount owed:
Rs.250.00 *
Minimum payment:
Rs.500.00
How to pay by Cheque or Demand Draft
Send a cheque or demand draft by courier to the Mumbai office of Citibank, our trusted payment partner, to add funds to your AdWords account. Just follow these three easy steps:
Write 'Google India Pvt Ltd- 9083676998 ' in the 'Pay' or 'In favour of' field of a cheque or demand draft.
example cheque
Write the amount that you want to be credited to your AdWords account in the 'Rupees' field.
Mail the Cheque/DD to:Drop Box CollectionsCitigroup Global Services Ltd1st Floor, Infinity TowersMindspace, Link RoadMaladMumbai - 400064.Phone Number: 022-6640 8179 / 8177
environmental managmenent - NITIE
M Sc., M. Tech., Ph. D. (Environmental Management),
Assistant Professor, Industrial Safety & Environmental Management
Area of Expertise
Corporate Environmental Management
Environmental Strategy
EMS based on ISO 14000 series (Qualified Lead Auditor)
Life Cycle Assessment & Design for Environment
Environmental Performance Evaluation · Environmental Accounting
Environmental Impact Assessment
Carrying Capacity Based Developmental Planning
Natural Resources Management
Sustainability and Business
Projects
Ministry of Environment & Forests sponsored project titled "Carrying Capacity based Developmental Planning of Doon Valley" at National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur.
Ministry of Environment & Forests sponsored project titled "Carrying Capacity based Developmental Planning of National Capital Region" at National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur.
CSIR Sponsored project titled "Applications of Fuzzy Logic Based Models in R&D Management" at D A University, Indore.
Ministry of Environment & Forests sponsored project titled " Life Cycle Assessment of Steel Sector in India, at National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur.
Ecological Damage Cost Estimation of a Hotel on the direction of Hon'ble Supreme Court of India ., at National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur.
Publications
1.Evaluation of Life Cycle Impacts using Elicited Societal Weights-a Case Study Shirish Sangle and P Ram Babu International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, Vol. 30, No. 4, 333-341.2. Neural Network Model for Identification of Societal Preference of Environmental Issues Shirish Sangle and P Ram Babu In Press. International Journal of Environment and Pollution.3.Redefining the Environmental Management System Boundaries through Stakeholder Management Across Product Life Cycle Shirish Sangle. In Press. International Journal of Environment and Sustainable Development.
4. Corporate Environmental Governance: From Shareholders to Stakeholders Shirish Sangle Presented in 10th International Conference of Greening the Industry Network: Corporate Social Responsibility-Governance for Sustainability, in Göteborg, Sweden during June 23-26, 2002. The abstract and the full paper is available at http://www.gin2002.miljo.chalmers.se 5. Framework for Assessing Stakeholder Satisfaction for better Corporate Environmental Governance Shirish Sangle and P. Ram Babu Proceedings of International Conference of Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management pp.229-238 at University of Leeds, UK during July 1-2, 2002.6. Choice of Valuation Methods in LCA: End Users' Perspective) Shirish Sangle Presented on-line in international e-conference 'InLCA/LCM 2002 Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Management' organized by American Center of Life Cycle Assessment and Institute of Environmental Research and Education (IERE), USA during May 20-25, 2002. Paper is available www.lcacenter.org/lca-lcm/session-methods.html7. Maximizing Benefits of Environmental Management System through Life Cycle AssessmentShirish Sangle and Arvind NemaPresented on-line in international e-conference 'InLCA/LCM 2002 Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Management' organized by American Center of Life Cycle Assessment and Institute of Environmental Research and Education (IERE), USA during May 20-25, 2002. Paper is available at www.lcacenter.org/lca-lcm/session-lcm.html 8. Evaluation of Life Cycle Impacts: Identification of Societal Weights of Environmental Issues in the National Capital Region of India. Shirish Sangle, P. Ram Babu and P. KhannaInternational Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 1999, Vol. 4, No. 4, 221-228
Teaching and Training
Subjects Taught at PG level
Corporate Environmental Management
Environmentally Conscious Manufacturing
Environmental Management System
Environmental Impact Assessment
SHE Systems: ISO 14000 and OHSAS 18000
Loss Prevention and Industrial Insurance
Services Marketing (coordinated)
Other Activities
Member, Sponsored R&D program of the Institute
Conferences and Seminars
Workshop/Seminar Organized
Organized a two day National Workshop on " EMS for Service Sector: Barriers and Interventions"during December 14-15, 2001 (Over 100 participants)
Organized a one day seminar on "Corporate Environmental Management" in partnership with US-ERC at World Trade Centre, Mumbai on June 29, 2001 (over 40 participants)
International Participation
10th International Conference of Greening the Industry Network: 'Corporate Social Responsibility-Governance for Sustainability', in Göteborg, Sweden during June 23-26, 2002.
International Conference of Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management at University of Leeds, UK during July 1-2, 2002.
International e-conference 'InLCA/LCM 2002 Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Management' organized by American Center of Life Cycle Assessment and Institute of Environmental Research and Education (IERE), USA during May 20-25, 2002.
Participated in three-day workshop on "Educate the Educator" on Corporate Environmental Management conducted by International Institute of Industrial Environment Economics (IIIEE), Lund University, Sweden during January 15-17, 2002 at Nagpur, India
Participated in a National Conference on 'Cost Benefit Issues of Cleaner Technologies' conducted by National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Mumbai, India during April 5-6, 2002
Participated in Workshop on "Training of Trainers and Consultant on ISO 14000" conducted by Asian Productivity Organization (APO, Japan) at Singapore during October 7-16, 1998.
Participated in a Indo-British Programme on 'Strategic Environment Assessment' at National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur, India during March 7-10, 1996
National Participation
As a resource person in one day orientation workshop titled "Infusing Environmental Concept into Business Curricula" organized at Shailesh J Mehata School of Management-IIT Mumbai, sponsored by Ministry of Environment and Forests on September 23, 2002.
Participated in a Seminar 'Trends in Cleaner Technologies' being organized by Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industries on May 27, 2002.
Participated in a National Conference on 'Sustainable Development-A System Dynamics Approach' conducted by System Dynamics Society of India at National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur, India during April 6-8, 1995
Consultancy
Associated in following consulting assignments
A World Bank aided project sponsored by PWSSB titled 'Assessment of Implementation Systems of Satluj Action Plan
Design and Development of Management Information System for a State Pollution Control Board
Awards
Senior Research Fellowship from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India for a period of four academic years (September 1994-August 1998)
Senior Research Fellowship a CSIR sponsored project at DA University, Indore in April 1994.· Senior Project Fellowship from the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur from September 1998 to August 1999
Awarded Sustainable Business Challenge Certificate from World Business Council on Sustainable Development, Switzerland in recognition for understanding the economic, social and environmental aspects of sustainability.
Awarded Global Business Scenario Certificate from World Business Council on Sustainable Development, Switzerland in recognition for understanding the implications of sustainability on global business environment.
Awarded Internship for three months by World Business Council on Sustainable Development, Switzerland at Environment Europe Center of Sony International, Stuttgart, Germany for period September -November 1998 (not availed).
Selected for International Visitors Programme by US government for training-cum-interaction with US Universities and industries for a period of one month - August, 2003 (not availed)
My Family
Contact me
' );
//-->\n
shirishsangle@faculty.nitie.edu
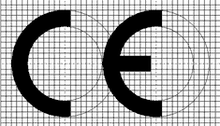
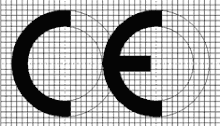
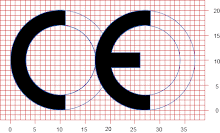
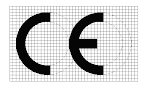
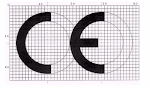
how to CE Mark: Medical Devices
By Nils Bromander
SEMKO (Centre for) Medical Engineering and Physics (Kista, Sweden)
General Requirements
All manufacturers must:
Classify the devices manufactured (Annex 9), except for those devices designed for special purposes or intended for clinical investigations (Annex 8).
Select and follow the appropriate conformity assessment procedure (Annexes 2–7), based upon the class to which the device belongs (Article 11; see summaries for each class below).
Ensure that the device fulfills the essential requirements (Annex 1).
Prepare technical documentation (Annex 2, 3, 5, or 7), including a general description of the product, design drawings, the results of the risk analysis, a list of standards applied, test reports, etc. This documentation should enable the assessment of the conformity of the product with the requirements of the directive.
Establish a system for reviewing data concerning products placed in the market, and implement appropriate means to take any necessary corrective actions.
Notify the authorities of serious accidents and/or narrow escapes from injury attributed to the product.
Issue an EC Declaration of Conformity.
File the EC Declaration of Conformity and the technical documentation, as well as all decisions, reports, and certificates from notified bodies, in such a way as to make the information available to the national authorities for a period ending no less than five years after the last product has been manufactured.
All products must:
Comply with the essential requirements.
Be provided with CE marking, except for custom-made devices and devices intended for clinical investigations.
Specific Requirements
Class I Products
The manufacturer must declare that the products concerned meet the provisions of the directive. The CE mark may then be affixed to the device (Annex 7).
The manufacturer or its authorized representative for the marketing of the product must register its activities with the competent authority of the member country in which the registered business is located.
An exception is made to this procedure for devices that are placed on the market in a sterile condition and/or have a measuring function. In such cases, the notified body shall examine the production process with regard to sterility and/or measuring function (Annex 4, 5, or 6).
Figure 1 is a flowchart showing the steps involved in CE marking for Class I devices.
Figure 1. Procedure for Class I products.
Class IIa Products
There are two alternative routes to CE marking for Class IIa devices. In alternative 1, the notified body must accept the manufacturer's total quality system (design, manufacturing, and final inspection) according to Annex 2, except for section 4.
In alternative 2, the manufacturer follows the procedure in Annex 7 (see above). In addition, the notified body examines and accepts each manufactured item/batch according to Annex 4 or accepts the quality system for production and final testing according to Annex 5 or the quality system for products according to Annex 6.
After taking the various administrative measures described in the relevant annex, the manufacturer may affix both the CE mark and the identification number of the notified body to the product. Figure 2 charts the procedure for Class IIa devices.
Figure 2. Procedure for Class IIa products.
Class IIb Products
Like manufacturers of Class IIa devices, manufacturers of Class IIb products may choose between two alternative procedures. In alternative 1, once again, the notified body must accept the manufacturer's total quality system (design, manufacturing, and final inspection) according to Annex 2, except for section 4.
In alternative 2, the notified body must examine and assess the documentation and type-test the product according to Annex 3 and examine and accept each manufactured item/batch according to Annex 4 or accept the quality system for production and final testing according to Annex 5 or the quality system for products according to Annex 6.
After taking the various administrative measures described in the relevant annex, the manufacturer may affix both the CE mark and the identification number of the notified body to the product. Figure 3 spells out the necessary steps for CE marking of Class IIb devices.
Figure 3. Procedure for Class IIb products.
Figure 4. Procedure for Class III products.
Class III Products
For Class III devices, once again, two alternatives are provided. In alternative 1, the notified body must accept the manufacturer's total quality system (design, manufacturing, and final inspection) and examine the design of the product according to Annex 2.
In alternative 2, the notified body must examine and assess the documentation and type-test the product according to Annex 3 and examine and accept each manufactured item/batch according to Annex 4 or accept the quality system for production and final testing according to Annex 5.
After taking the various administrative measures described in the relevant annex, the manufacturer may affix both the CE mark and the identification number of the notified body to the product. Figure 4 illustrates the routes to CE marking for Class III devices.
Back to 1999 Annual Reference Guide Table of Contents
Source
Saturday, December 12, 2009
Why do indians earn more and spend less?
its not just money, we chase Lakshmi
Lakshmi ke liye kucch bhi karega
and it dont make sense to spend dollars in the US of A
In India a dollar is worth 50 bucks
in India u dont pay for a pee
its free on the roads
and u can even take a shit too
u can do more with a dollar
go here
Friday, December 11, 2009
Healthcare in India
AIIMS' students educating slum dwellers in Delhi about water-borne diseases.
Healthcare in India is the responsibility of constituent states and territories of India. The Constitution charges every state with "raising of the level of nutrition and the standard of living of its people and the improvement of public health as among its primary duties". The National Health Policy was endorsed by the Parliament of India in 1983 and updated in 2002.[1]
The art of Health Care in India can be traced back nearly 3500 years. From the early days of Indian history the Aryurvedic tradition of medicine has been practiced. During the rule of Emperor Ashoka Maurya (third century B.C.E.), schools of learning in the healing arts were created. Many valuable herbs and medicinal combinations were created. Even today many of these continue to be used. During his rein there is evidence that Emperor Ashoka was the first leader in world history to attempt to give health care to all of his citizens, thus it was the India of antiquity which was the first state to give it's citizens national health care.
In recent times India has eradicated mass famines, half of children in India are underweight, one of the highest rates in the world and nearly the same rate of Sub-Saharan Africa. Water supply and sanitation in India continue to be a challenged, only one of three Indians has access to improved sanitation facilities such as toilet. India's HIV/AIDS epidemic is a growing threat. Cholera epidemics are not unknown. The maternal mortality in India is the second highest in the world.
Providing healthcare and disease prevention to India’s growing population of more than a billion people becomes challenging in the face of increased competition for resources. 2.47 million people in India are estimated to be HIV positive. India is one of the four countries worldwide where polio has not as yet been successfully eradicated and one third of the world’s tuberculosis cases are in India [2].
According to the World Health Organization 900,000 Indians die each year from drinking contaminated water and breathing in polluted air [3]. As India grapples with these basic issues, new challenges are emerging for example there is a rise in chronic adult diseases such as cardiovascular illnesses and diabetes as a consequence of changing lifestyles [4].
There are vast disparities in people’s health even among the different states across the country largely attributed to the resource allocation by the state governments where some states have been more successful than others. Better efforts are needed by the local governments to ensure that the health services provided are actually reaching the poor in worst-affected areas.
However, at the same time, India's health care system also includes entities which are world class. The Apollo set of hospitals are considered amougst Asia's most advanced hospitals. Many patients seeking treatment from even from Pakistan have come here. In November 2008, a Pakistani girl was operated on for heart problems. Thus, India's health care system has progressed and is a leader in South East Asia.
Contents[hide]
1 Medical professionals
2 Diseases
3 Issues
3.1 Malnutrition
3.2 Women
3.3 Water and sanitation
4 Healthcare Infrastructure
5 Central government role
6 Expenditure
7 Primary services
8 Health Insurance
9 Medical Tourism
10 Rate of growth
11 See also
12 References
13 External links
Equinox Analytics
Source
Thursday, December 10, 2009
GMP Guideleines
 | Good Manufacturing Practices |
GENERAL
- Name of the Company
- Date of Incorporation
- Is the Company acting as an Organization
- Regulated Sectors : Drug License Number and validity, Laboratory Registration & Categories of Drugs permitted
- Do the Company have a policy of customer satisfaction (quality policy)? If yes, obtain a copy of the same and attach.
Show Its Various Functions, Their Interrelation and Responsibility Control
| S. No. | Function | Functional Head(Mr./Ms./Mdm) | Age, Education, Training & Experience | Record of Qualification /certification by Drug Controllers |
| 1 | Management (Function of Planning that Includes Control of All Resources e.g., Investment, Banking & Finance, Human Resources and Legal Compliance) | |||
| 2 | Product Development & Technology (Including Standardization of Quality Plan, Specification and Processes) | |||
| 3 | Marketing, Sales and Distribution (Includes Warehousing) | |||
| 4 | Production | |||
| 5 | Purchasing & Stores of Incoming | |||
| 6 | Inspection and Quality Control (Including Setting up Assurance Standards) |
- Number of Production Supervisors Asst. mfg. Chemist.
- Number of Analysts
- Are production and quality functions independent of each other.
- Are all sections adequately staffed (supervisor/Asst. Mfg. Chemist) taking into consideration the works load.
- Is recruitment of an employee proceeded by medical examinations.
- What is the periodicity of subsequent medical examinations.
- Is an employee whose state is doubtful immediately removed from work side until he is fully recovered.
- Do all personnel receive GMPs training check course content of training.
- Is training documented.
- What is the periodicity of training.
- Are protective steps against likely damage to health due to occupational hazards satisfactory.
- Are there any sources of pollution in the neighborhoods of the building.
- Is plant layout of suitable size, design and construction sufficient for production and quality control of drugs being produced.
- Any person drain blocked sewer of public lavatory nearby.
- Is their adequate space for equipment, material and movement of personnel and materials.
- Is there any programmed to check entry of birds, rodents and insects.
- Are any products other than drugs manufactured in the same building.
- Are buildings & facilities properly constructed to facilitate adequate cleaning and sanitation.
- Are lighting and ventilation adequate.
- Are facilities for changing street clothes footwear, washing & toilets adequate and satisfactorily maintained.
- Are sewage, trash and other effluent disposal adequate whether production of penicillin’s/ B-Lactum Antibiotics have been segregated.
- Whether production of other specified products like hormones, cylotoxic drugs segregated or whether production is carried out on campaign basis.
- State of maintenance of building (check whether the firm/company have preventive maintenance program)
- Are floors, walls and ceilings properly constructed and easy to clean, maintain and disinfect.
- Are there physically segregated areas for Raw Materials & Packing Materials.
- Is their quarantine area for incoming raw Material
- Is their segregated area for rejected material
- Are there separate areas for materials requiring Special storage conditions e.g. Controlled temperature & Flame Proof
- Are the areas adequate for storage of the materials in relation to their a amount and facilities provided
- Do all containers of active RM excepients and intermediates bear appropriate label at all stage of manufacture?( In no give details)
- Are empty containers freed of old labels and checked immediately prior to use.
- Is lighting and ventilation adequate in Warehouse
- Have the areas requiring special storage conditions provided with monitoring devices and data maintained.
- Is there any program for general housekeeping.
- Is there any evidence of entry of insects Rodents & birds.
- Are their warehousing operating instructions.
- Are these instructions being followed.
- Are there labels for materials of different status i.e. quarantine tested and released for use and rejected
- Are there labels of different colors.
- Are labels on containers of RMS to be used in manufacture checked with regards to identity, quantity & CA approval? If no, give details.
- Are there the following informations on labels.
-Name of Material
-Batch Number
-Analysis number
-Date of release/rejection
-Date of expiry
-Date of testing - Do Quality Control personnel perform the sampling.
- Are their sampling procedures.
- Are there the following informations of each sample taken.
-Name of person who performed sampling?
-Number of samples taken?
-Number of containers sampled?
-Dated of sampling? - Are the containers provided for storage of raw materials suitable to preserve the quality.
- Is there stock rotation program (i.e. FIFO).
- Are the printed packing materials stored in orderly manner and well separated to prevent mixing.
- Are they recorded on stock cards register.
- Are enclosed and locked areas provided for storage of narcotic or highly toxic drugs.
- Is exterior storage available
-Solvent storage area.
-Inflammable material storage area
-Whether safety measures provided have
-Been assessed by regulatory agency if any?
-Are SOP’s available for handling of these :
-Materials
- Is the weighing area segregated.
- Are lighting and ventilation adequate.
- Is the area clean.
- Do the personnel wear appropriate clothing.
- Is their danger of cross contamination during weighing.
- Are the scales & balances calibrated regularly and records maintained.
- After the containers of the raw materials to be weighed, cleaned before opening.
- Are the raw materials for each batch, after weighing properly identified.
- Are adequately clean and dried equipment used for dispensing materials from the containers.
- Is the equipment adequate for intended use?(State size, capacity and check batch size)
- Is it constructed in such a way that lubricant coolant, etc. cannot contaminate the drug product.
- Does the equipment permit cleaning and maintenance
- Does the equipment show its status i.e. clean dirty, bath contents.
- Do all apparatus equipment bear appropriate labels to identity the product for which the equipment is used, its batch no., date etc.
- Are SOPs available for cleaning maintenance and sanitation.
- Are logbooks maintained for cleaning maintenance and sanitation of major equipment
- Are SOPs readily available to operators.
- If automatic electronic or mechanical equipment is used, are there?
-Written Programmes for calibration inspection?
-Records of such programmes?
-Checks to ensure that any changes are
-Made only by authorized person?
- Are airs handling units adequate and properly located and functional.
- Is air conditioning system adequate and functional.
- Are steam generation facilities adequate and functional.
- Are vacuum systems adequate and functional.
- Is compressed air system adequate and properly functioning.
- Is water supply system adequate? Check whether
- MCD or Tube well supplies. If tube well supply Whether potable.
- Is distilled water quality and supply system adequate.
- Is demineralised water quality and supply system adequate.
- Sanctioned Power___________HP
- Generator _________________KVA provided
- Are cleaning schedule available for
-Floors?
-Walls?
-Ceiling?
-Doors and windows?
-Electrical fittings? - Are SOPs available for cleaning and sanitization.
- Are disinfectants used rotated.
- Are logbooks maintained for cleaning and sanitation.
- Is microbial load monitored in different section.
- Are adequate facilities available for personal hygiene before entering into production area.
- Are personnel instructed to observe personal hygiene.
- Are clean sterile protective clothing’s changed every time a person enters sterile area.
- Are cleaning schedule available for
- Are alterations to processes recorded and authenticated by competent authorized persons
- Is an appropriate in process control being performed.
- Are non-sterile products tested for microbial load & whether microbial load is less than limits recommended by WHO.
- Are adequate measures taken to prevent cross contamination during production of different products in the same facility.
- If drying ovens are used Whether one product is dried at one time
- Are instruments used for temperature, pressure or other recording calibrated periodically and records maintained.
- Are semi finished products stored properly and are identified.
- Is stage of manufactured clearly indicated on containers.
- Is quality of water monitored, The following points may be checked.
-Source of Water?
-Is it potable?
-In case deiorized water, source of feed water?
-Frequency of charging columns, sampling
frequency?
-In case of water for Injection information like
-Is it prepared by distillation or reverse osmosis?
-Whether storage temperature is maintained at not less than 800 C and circulated. - Do the containers and closures meet required secifications.
- Are containers checked for cleanliness and suitability for packaging before use.
- Are containers of intermediates and FPs intended for use in the plant closed properly.
- Is homogeneity maintained during filling of ointment, creams and lotions.
- Are the following controls carried out during filling operations
-Check of volume, weight or counts.
-Visual inspection of empty and filled containers
-Visual inspection of closures - Is their adequate separation of packaging lines to prevent mix-ups.
- Is each line identified with name of the product batch no. and packaging size.
- Is there only one batch of product on packaging line at any given time.
- Is an inspection carried out of each packaging line before labeling and packing operation.
- Is the inspection verified by quality control.
- Is significant discrepancy in actual yield investigated.
- Is inspection carried out of each packaging line after operation to ensure that all excess/rejected labeling material area removed.
- Are all excess or rejected coded labels and cartons destroyed.
- Is batch production record prepared for each batch of product and maintained.
- Do the batch production records indicate that each significant step in manufacturing was performed and checked by second individual wherever appropriate.
- Are master instructions or procedures readily available in production area.
- Are these instructions and procedures being followed.
- Are only materials, containers and appliances necessary for the job in hand stored in the vicinity of the manufacturing areas and are these properly labeled with name of the product, batch no. date, etc.
- In inert gas used in any operation including packing.
- If yes, identify the gas and the products for which Used.
- Is specimen copy of each label and printed packaging material approved before sending it to the printer
- Are labels and other printed packing materials checked and approved by Quality Control before release to productions.
- Is access labels and other printed packaging material store limited to authorized persons.
- Is there any designated individual to control and issue labels and other printed packaging materials.
- Are individual labels stored separately.
- Are printer’s counting accepted or counted by factory workers for inventory purposes.
- Do batch production records indicate
-Number of labels or other printed
-Batch or control code?
-Reconciliation of number/amount of label and printed packing material issued, used and destroyed?.
- Are master control procedures Signed and dated by responsible person.
- Do these control procedures included specifications, test procedures or other control procedures for:
-Raw materials?
-In-Process materials?
-Packaging and labeling materials?
-Finished products? - Are the procedure in written form and readily
Available to QC personnel. - Are there procedures and specifications for acceptance of reprocessed materials.
- Are there written sampling procedures for
-Raw materials?
-In process material
-Packaging and labeling materials?
-Finished Products? - Are samples collected by Q.C. personnel
- Is there special room for microbiological and sterility testing.
- Is the environment of room controlled.
- Cultures, Sub Cultures
-Are microbial stains obtained from authorized/reputed source?.
-Frequency of sub-culturing
-Frequency of identification of organism by microscopically or biochemical test.
-Are records of subculturing and identification of strains maintained? - Are animal test performed.
- Are animals properly housed.
- Are the temperature and humidity of animal house controlled.
- Are records of animals used maintained.
- Are the animal quarantined on receipts and examined for infection/disease.
- In access to animal house restricted to authorized persons.
- Is fresh water and animal feed available in animal house
- Are all raw materials, containers, closures, labels and printed packaging materials approved and released by Q.C. for use in manufacture of drug products.
- Are semi finished products tested for appropriate tests when necessary.
- Is bulk finished products tested for established specifications before packaging.
- Is every finished products tested for established specifications before release for sale.
- Are there any deviations from established procedures or specifications and are these justified.
- Does the QC maintain records of all the test carried out.
- Does the QC reviews all production and control records to ensure compliance with established written procedures before a batch of the products is released for sale.
- Reference standards
(a)Are reference standards(R.S.) available?
(b)Are these primary or working R.S ?
(c)Are working RC calibrated against primary R.S. or CRS ?
(d)Is R.s. stored properly (at low temperature under dehumidified conditions)?.
(e)Are records of R.S. their calibration maintained? - Are samples in sufficient quantity for testing twice retained of starting materials and finished products for future examination, in case of need.
- Is written program available for stability studies including the following
-Sample storage condition?
-Room temperature?
-Accelerated again test?
-Sample size and test intervals?
-Reliable and specific test methods?
-Testing in the same containers closure system in which it is marketed?
- Is the area adequate with reference to materials stored.
- Are lighting and ventilation adequate.
- Whether special areas with temperature and humidity control required? Have these been provided.
- Is their stock rotation program (FIFO).
- Are the inventory records to show
-Amounts?
-Batch Number ?
-Date of receipt ? - Have distribution records been maintained.
- Do distribution records provide sufficient information for drug recall purpose.
- Is there segregated are for retrieved goods.
- Are SOPs available for the following
-Receipt of raw materials and other components?
-Quarantine and storage?
-Quality Control System and approval/ rejection?
-Release to production?
-Weighing and dispensing ?
-Processing and production operations?
-Packaging and labeling ?
-Quality Control?
-In Process
-Finished Products?
-Storage of Finished Products?
-Distribution?
-Returned goods?
-Recall and complaints?
-Cleaning and maintenance ?
-Quality control of Water
-For reworking of nonconforming batches in existence? If yes, check records - Have these SOPs been prepared, signed and dated by responsible person.
- Are there additional documents like logbooks notebooks or other similar records available to show execution of various functions.
- In case of review and changes, does responsible person singe SOPs and do these show their date of effectiveness.
- Are there records of receipt of raw material sand
Do these have following information?(Goods Receipt Note-GRN)
-Receiving GRN documents number?
-Date of receipt?
-Manufacturer?
-Manufacturers batch number?
-Type and size of containers?
-Number of containers and conditions? - Are there records of stock and issue of raw materials and do these have following information:
-Opening balance
-Date of receipt
-Quantity received?
-Name and batch number assigned by the manufacturer?
-Invoice number, date, name and address of supplier?.
-Analysis report number and date
-Date of expiry
-Date of issue?
-Name and batch number of product for manufacture of which issued?
-Balance?
-Signature of issuing person? - Is there a master formulation record for each drug product being produced.
- Is there as separate master production documents for each dosage form/batch size
- Are these master production records signed and dated by competent person? Do they show the following particulars.
-The name, strength and description of the dosage form?.
-Name and quantity of each active ingredient per dosage unit or per unit of weight or measure of the drug product?
-The total weights or measures of any dosage unit?.
-A complete list of components identified by name the /codes?.
-An accurate statement of the quantity of Each component?
-Calculated axcess of component, if any?
-Theoretical weight or measure at appropriate processing stage?
-Description of containers, losures and packaging materials?
-Complete manufacturing instruction?
-Sampling & testing procedures including in-process controls?
-Specification & precautions to be taken? - Is a batch production records prepared for every batch produced.
- Is it reproduction of the appropriate master production documents or it has all critical information about the batch.
- Has it been checked for accuracy signed and dated by a responsible person.
- Are the records maintained by QC for all the test carried out.
- (xiii)Do these records include:
-Graphs charts, spectra etc.?
-Calculations?
-Signatures of individuals who performed the test?
-Signature of the designated person
responsible for the review of the records for accuracy and compliance with established standards? - Are other associated records available.
- Is documentation available readily for examination.
- Where errors have been made in entering or transcribing data
-Have errors been crossed out with one line?
-Have corrections been made above those crossed out?
-Are corrections dated and initialed? - Are batch production records capable of giving complete history of the batch right from the RM stage to the distribution of FP.
- Are the balances calibrated routinely.
- Have measuring equipments been calibrated.
- Have thermometers / thermocouples been calibrated? (Temperature at which calibrated)
-Minimum
-Maximum - Have the pressure gauges been calibrated.
- Are instruments routinely calibrated.
- What is the periodicity of calibration.
- Are records maintained for all calibration.
Note : Draw a list of all major instruments available and Check calibration records.
- Are validation studies carried out for the following
-Cleaning and sanitation procedures?
-Process?
-Testing? - Have qualification studies been carried out for equipment before validation studies.
- Are validation protocols available for validation studies.
- Do the validation reports show recorded resultsand conclusions.
- Are validation studies carried out periodically.
- Is revalidation carried out in event of significant change in materials(s) or equipment.
Note : Check a few qualification and validation studies in details.
- Are their written procedures for handling complaints.
- Is an investigation carried out wherever necessary including discussion with manufacturing personnel.
- Does QC review complaints.
- Is there a designated person for overall evaluation
- Are records maintained for complaints and do these include the following
-Name of the product with strength?
-Batch Number
-Name of complainant
-Nature of complaint? - Is a report of investigation made.
- Do qualified personnel evaluate complaints involving adverse reactions.
- In case of significant adverse reactions, are appropriate Health Authorities notified.
- Is their written procedure for product recall in case of products know of suspected to be defective.
- Is there a designated person responsible for execution and coordination of product recalls.
- Have the degrees of recalls been specified (i.e Degree 1, Degree II and Degree III)
- Is the following information available
-Fax, Telex, telephone numbers and addresses or national, regional and local regulatory authorities?
-Fax, Telex, telephones numbers and addresses of radio, television and press agencies?
-Fax, telex and telephone numbers and addresses of distributors, wholesalers, hospitals, etc.?
-Fax, Telex and telephone numbers and addresses of competent authorities of the countries to which the drug products are exported? - Is there as system so that distribution records are readily available to the designated person responsible for product records.
- Is the progress of product recalls recorded and final report issued including reconciliation bettween the delivered and recovered quantities of the product.
- Is the effectiveness of product recalls evaluated from time to time.
- Is there a segregated are for recalled products.
- Are written procedures available for receipt and control of returned products.
- If reasons for returning the product implicated other batches are an investigation made and report prepared.
- Are returned or salvaged drug products destroyed unless QC determines their reprocessing.
- Are records of returned products maintained including their disposition.
- Are there written procedures for reprocessing and do these include
-Specifications and characteristics for approval?
-Identification of batch to reflect reprocessing?
-Revised stability data, if necessary
- Is a safety manual available.
- Are safety equipment, shoes, goggles, glove, showers, aprons, masks, breathing apparatus, etc., available in the factory.
- Is adequate first aid equipment available at convenient place in the factory.
- Is adequate first aid equipment available at convenient place in the Factory.
- Is periodic first aid training given to staff
- Is flame - proof equipment used where flamable solvents or materials are stored or handled during manufacture.
- Is adequate fire fighting equipment like fire extinguishers, ladders, fire buckets filled with water/sand, etc., available.
- Are staffs trained in fire fighting operations.
- Is the building safe and provided with emergency exit, escape routes ladders, etc.
- Does the firm maintain accident history/records? if yes, comment on its adequacy.
- Are arrangements for the following adequate.
- Disposal of solid/semi-solid waste.
- Disposal of sewerage.
- Disposal of liquid laboratory waste.
- Management of gaseous pollutants.<.li>
- Is effluent treatment plant is existence? If yes, comment on it.
- Are fume hoods of adequate design in existence and used wherever necessary.
- Is the report of previous self-inspection available.
- Recommendations of previous self-inspection.
- Whether corrective measures have been taken as recommended by previous self-inspection team.
Source












.jpg)





.jpg)

.jpg)








.jpg)

.jpg)













.jpg)


.jpg)









































































































































































































.jpg)

.jpg)











.jpg)















































.jpg)















.jpg)
























































































































.jpg)